- have liver problems
- plan to have surgery
- have chicken pox or measles or have recently been near anyone with chicken pox or measles
- have an infection
- have high blood sugar levels (prediabetes or diabetes)
- have glaucoma or cataracts
- have a family history of diabetes or glaucoma
- have or have had tuberculosis
- have high blood pressure (hypertension)
- have decreased bone mineral density (osteoporosis)
UNDERSTANDING THE GUT-KIDNEY CONNECTION IN IgA NEPHROPATHY (IgAN)
What is IgAN?
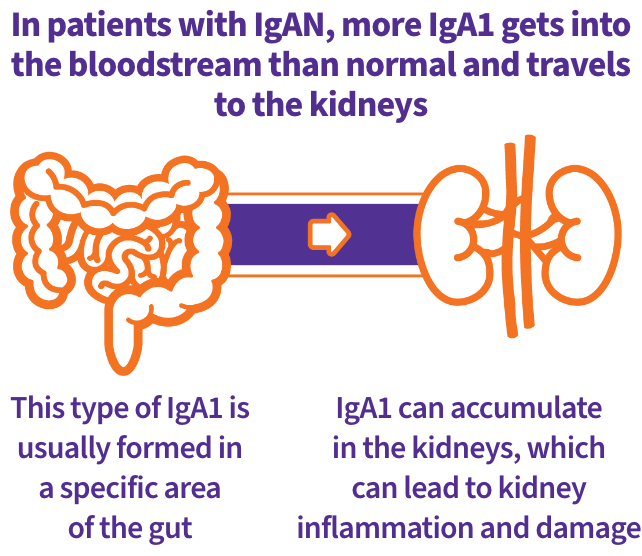
IgAN is a progressive autoimmune disease affecting the kidneys. In patients with IgAN, too much of an antibody known as IgA1 builds up in your kidneys, leading to inflammation and damage.
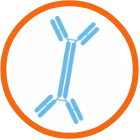
IgAN is caused by increased levels of a type of IgA1 in the blood
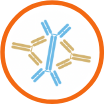
The body produces antibodies to IgA1
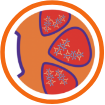
Clusters of these autoimmune complexes are deposited in the kidney

The kidneys become inflamed, and irreversible damage can occur
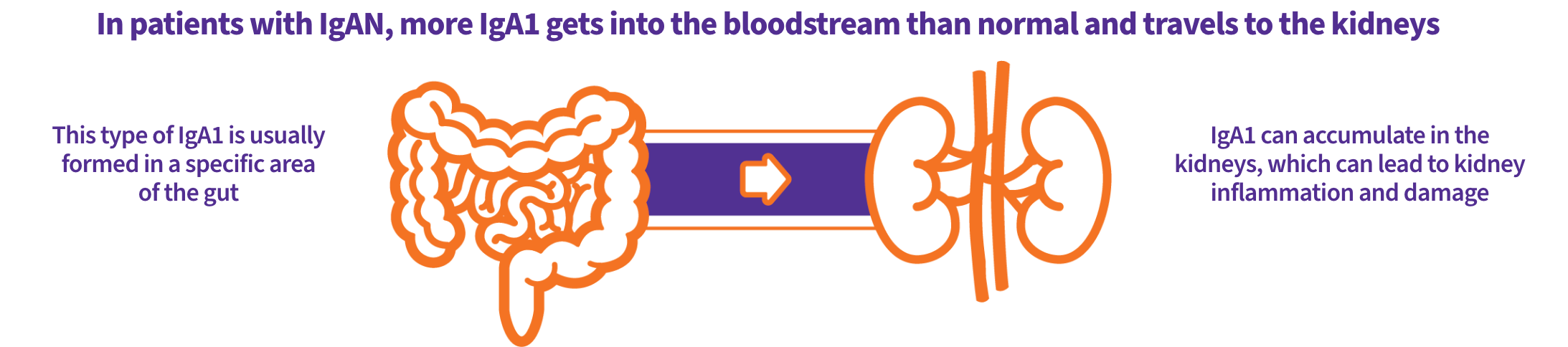
What may cause IgAN?
Even though the kidneys are the end-organs damaged in IgAN disease, it is not the only organ thought to be involved. One of the main underlying causes of IgAN is thought to be the IgA1 antibody, which is most often produced in the gut.
WHAT ARE THE POTENTIAL SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF IgAN?
Although IgAN is often asymptomatic in early stages, you may experience the following:
Lower back pain

Blood in the urine

Foamy urine due to excess protein
Swelling in feet, ankles, or legs
These symptoms may be subtle, and you may not experience any of them. Excess protein in the urine, also known as proteinuria, or even blood in your urine may not be discovered until a routine urine test. A kidney biopsy by your doctor is needed to confirm a diagnosis.
HOW IS IgAN DIAGNOSED?
A diagnosis of IgAN is confirmed with a kidney biopsy


- A kidney biopsy is a procedure that involves taking a small piece of kidney tissue for examination
- A biopsy may reveal IgA deposits in the glomeruli
- The biopsy can also show how much kidney damage has already occurred
HOW IS IgAN MONITORED?
Two important measures for people with IgAN are eGFR and UPCR.

eGFR
Estimated glomerular filtration rate
is a measure of kidney function. The higher the number
(the range is 0 to 120), the better your kidney function.
This is considered a useful measure of overall kidney
function.

UPCR
Urine protein-to-creatinine ratio
is a test to measure the amount of protein in the urine.
High protein in your urine, or proteinuria, is considered a
risk factor for disease worsening.
Some studies have shown a correlation between eGFR and UPCR. For example, higher UPCR may be associated with a higher risk of kidney failure and greater average loss in eGFR.

